Work has become an integral part of the world in which we live. Most people work very hard, so regular visits to the doctor for a full health check are a thing of the past.
However, it is important to monitor vital body functions. So today we’re going to look at one of the vital signs, blood pressure, what it means and how you can check it at home without equipment. You’ve probably heard a lot about blood pressure and the importance of keeping it at a normal level.
Knowing that your body is functioning properly is one of the most important thing you have to pay attention to.
Understanding What Blood Pressure Is
Basically, blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of the blood circulating in the walls of blood vessels. This pressure is caused by the contraction of the heart muscle.
A more simple explanation is, when the heart beats, it supplies the body with blood, providing the body the necessary energy and oxygen. When blood moves, it exert pressure on the walls of the blood vessels. The strength of this pressure is blood pressure.

Blood Pressure Reading, Expression And Unit Of Measurement
Determining blood pressure and units is easy. Blood pressure is usually expressed in two numbers: systolic and diastolic. The first (systolic pressure) is the maximum pressure when the heart contracts, and it is highest. The second (diastolic pressure) is the lowest pressure and its when the heart relaxes between two contractions of the heart muscles.
Both systolic and diastolic pressures are measured in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the ambient atmospheric pressure.
The ideal blood pressure is 90/60 to 120/80 mmHg. Let’s say you have checked your blood pressure and it reads 90/70 mmHg. The first number “90” is referred to as your systolic pressure and the second number “60” is referred to as your diastolic blood pressure.
If both of these pressure is too high, it means that the pressure in your arteries and heart is too high. This is called high blood pressure and can lead to acute heart attacks and even strokes.
The following chart is a guideline for the diagnosis of different stages or categories of hypertension published by the American College of Cardiology in November 2017.

These guidelines emphasize the importance of using the correct blood pressure measurement technique. It is advisable to monitor blood pressure at home using approved equipment for accurate readings since high blood pressure is a silent killer.
The committee emphasize the importance of proper training of healthcare providers so that they can identify “white high blood pressure.” Therefore, it is important to monitor your blood pressure and make sure it is not too high.
To achieve this you would have to check yourself regularly at home or in a medical facility with handcuffs to see if your blood pressure is normal.
Also, you can easily check your systolic blood pressure at home and get an estimate without a blood pressure monitor. However, without equipment, it is impossible to measure diastolic blood pressure.
For your safety, you have to use the right blood pressure equipment when checking your blood pressure at home. You would have visit a healthcare facilities to check if you don’t have the approved equipment.
That being said, let’s look at how you can check your systolic blood pressure at home. It takes only three steps.
Steps Involved In Checking Blood Pressure (Systolic Pressure) At Home Without Equipment
You can easily check your systolic blood pressure by following these 3 steps:
Step 1: Look For Your Radial Artery
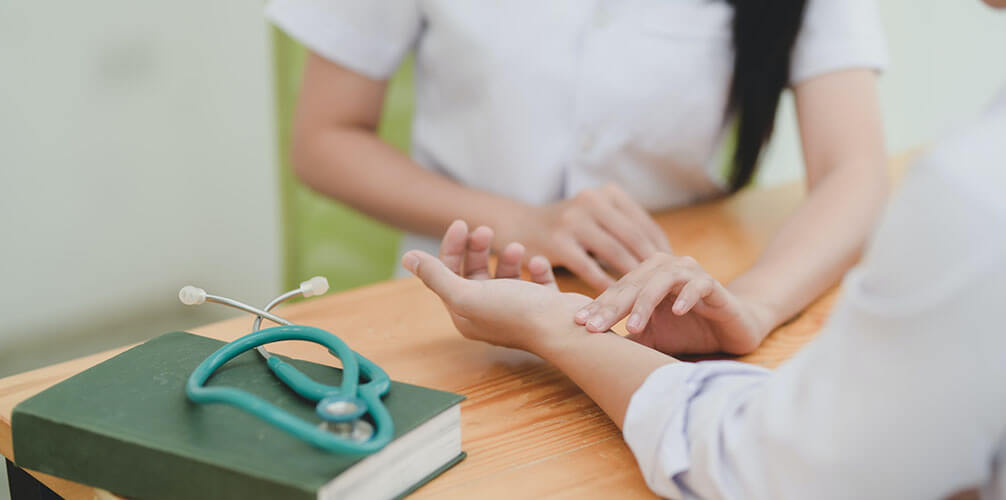

To do this, you first need to determine the heart rate in the left hand by looking for what is called the radial artery. Locating the radial artery would help you arrive at a palpable radial pulse. This will give you the basic information you need to know if your systolic blood pressure is normal.
The radial artery is located under the thumb and slightly above the wrist.
It is important to understand that this is a rough estimate that you will only get if your systolic blood pressure is not low. If you feel the pulse without problems, then the pressure in the pump is 60-80 mm Hg.
To do this, you first need to determine the heart rate in the left hand by looking for what is called the radial artery. Locating the radial artery would help you arrive at a palpable radial pulse. This will give you the basic information you need to know if your systolic blood pressure is normal.
The radial artery is located under the thumb and slightly above the wrist.
It is important to understand that this is a rough estimate that you will only get if your systolic blood pressure is not low. If you feel the pulse without problems, then the pressure in the pump is 60-80 mm Hg.
- Place two fingers, preferably index and middle, under the folds of your wrist, next to your thumb.
- Do not use your thumb as it has a strong enough pulse to prevent this from happening.
- If you feel a sharp pulse, it means that your systolic blood pressure is above 80 mmHg.
Step 2: Look For Your Carotid Artery

The second step is to find the carotid artery that runs through the neck. Please see the diagram above.
Again, it’s important to understand that this is a rough estimate that only tells you if your systolic blood pressure is not low.
- Press lightly until you feel a pulse.
- Do not press too hard as this restricts blood flow.
- A palpated pulse on the carotid artery means that the heart is pumping a pressure of 60-70 mm Hg.
Step 3: Look For Femoral artery
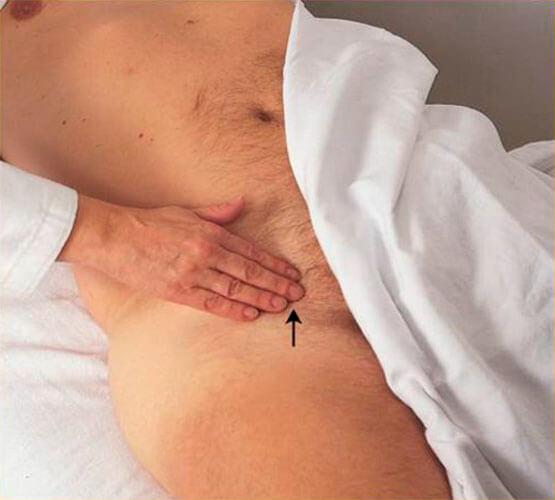
It is excreted from the stomach through the thigh. See the diagram above. This gives a light sensation to the centre of the thigh and both sides of the abdomen.
You can equally palpate yours by placing your index and middle finger between the abdomen and the thigh as shown in the diagram above.
Note: Blood pressure here is relatively low. In most patients with palpable femoral pulse, the minimum systolic blood pressure is 70-80 mm Hg.
Very Important:
Do not press too hard when you feel different arteries when trying to palpate them. This is very important because too much pressure on these blood vessels, especially the carotid artery, can lower blood pressure in the veins and cause dizziness. Calm down and relax before checking your blood pressure. Any strain can interfere with blood pressure measurement.
Disclaimer:
This content, including tips, is for general information only. This is not a substitute for a qualified medical opinion. Always ask your specialist or doctor for more information. NIGHTINGALE KNOWS is not responsible for this information.






